
- Google Bare Metal Solution
Google Bare Metal Solution
Matthew Hampton, Dito April 2022

Migrating Legacy Oracle Applications to the Cloud
Most enterprises are realizing the infrastructure, licensing, and operational cost savings of leveraging the cloud. However, not all cloud solutions work with Oracle and its licensing structure. Licensing, patching, and physical hardware requirements need to be considered when finding a cloud solution.
There are a number of options. AWS and Azure offer managed service solutions for Oracle database workloads. These can be a good choice for isolated database workloads that are not tightly coupled to other system components. AWS’s RDS offering can be cost effective for running Standard Edition. Oracle’s licensing policies make it less attractive for Enterprise Edition customers. These make it more expensive to run in AWS than your own data center or Oracle’s cloud.
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) is an obvious candidate for running Oracle workloads in the cloud. Oracle was a late entry to cloud computing and has spent a number of years playing catch-up. Its current offering is arguably still behind the competition but good enough for most. The main problem with OCI is Oracle itself. The company has a history of using vendor lock-in and aggressive sales techniques to extract revenue from its customers. Few of its customers relish the prospect of an increased dependency on them.
Many would settle for a solution that allowed them to move Oracle workloads “as-is” to the cloud and continue using their existing licenses. Google Bare Metal Solution provides this.
What is Google Cloud BMS?
Google Cloud BMS is a colocation offering that allows customers to migrate their Oracle workloads into the cloud with support for RAC and older database versions. Customers sign a 1, 2 or 3 year commitment to lease the BMS hardware which Google purchases on their behalf. At the time of writing the hardware options varied from an 8 core machine with 192GB of RAM to 448 cores and 24TB RAM. Customers are responsible for the software, applications, and data that they use and store in the BMS environment.
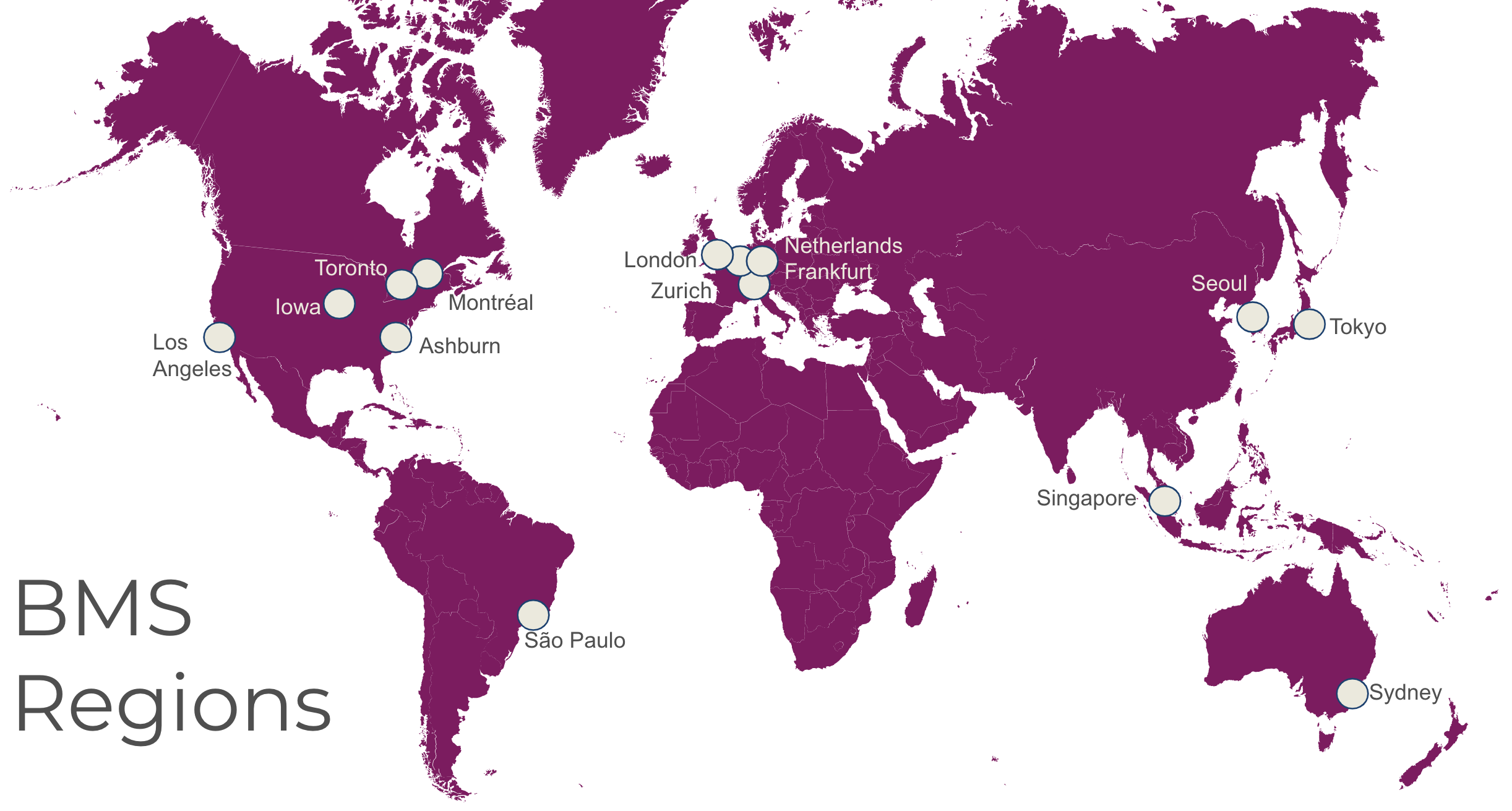
Region Extension
You lease dedicated hardware for fixed terms in data centers, distinct from, but geographically close to a Google Cloud data center. Google calls these data centers region extensions.
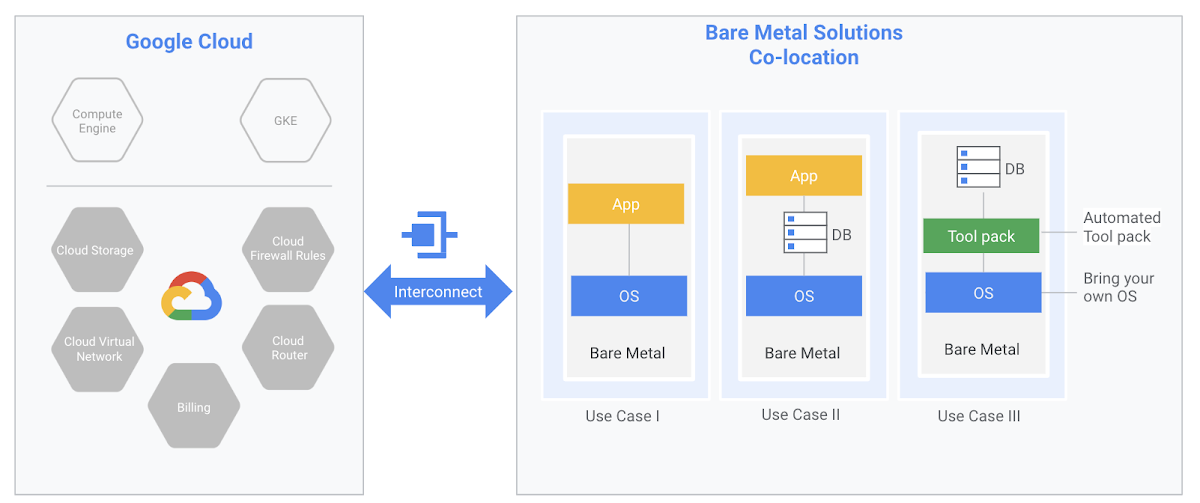
BMS provides enterprise grade x86-64 server hardware to run specialized workloads with low-latency access to Google Cloud services. Google manages the server hardware, networking, facilities, and other core infrastructure. This leaves you to focus on your application, and how you want to configure it.
Latency between each region extension and its nearest Google Cloud region is less than 2 milliseconds round trip. Applications can run on bare metal or in a Google Cloud region. Google has long term plans to provide a region extension in every Google Cloud region.
Hardware
Hardware is available in a number of “Tee-shirt” sizes as shown in the diagram below.
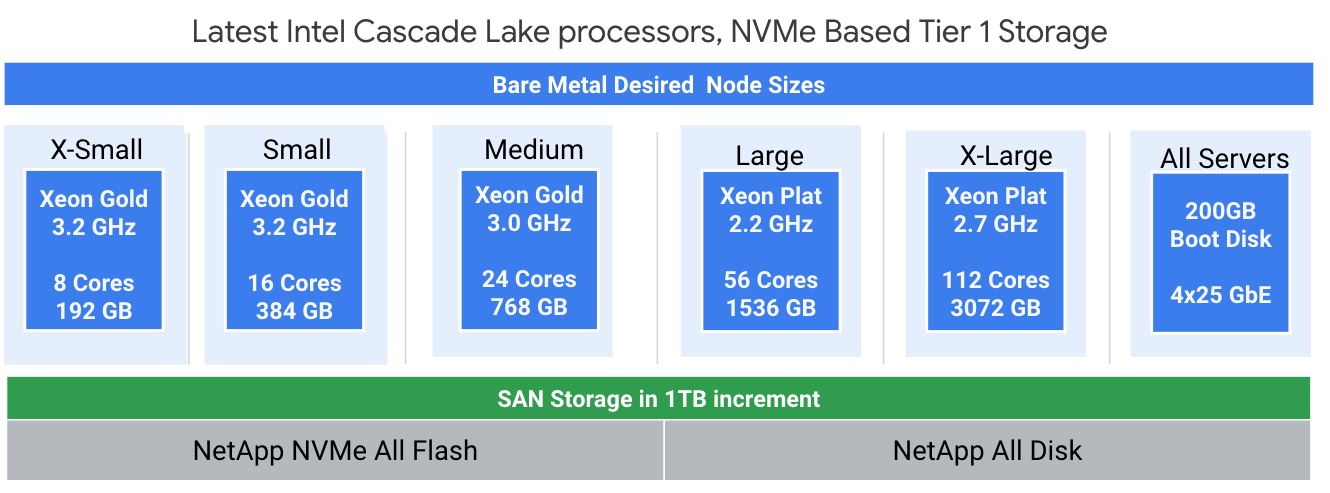
Specs:
- Atos BullSequana S servers
- Intel Cascade Lake processors running Linux or Windows
- Redundant NICs
- Four 25 Gbps NICs, jumbo frames supported
- Public and private networks for RAC
- SSD or HDD storage options
Storage
Netapp SAN optimally configured for Oracle is available in 1TB increments. Storage is provisioned and tuned as per NetApp’s best practices for Oracle database (FC SAN). Customers specify their desired IOPS, storage requirements, and LUN configuration. Quality of Service assurances of up to 400,000 IOPS are available.
- NetApp systems use either RAID-DP (double parity, similar to RAID6 - on the flash systems) or RAID-TEC (triple parity - on disk systems). That means that all volumes will span across those raid groups.
- All storage components are fault tolerant. LUNs reside on an HA-pair which ensures redundancy in case of storage node failures. All LUNs are accessed on multiple paths, in 2 FC fabrics, which offers redundancy on the front-end side.
- Each volume spans at least 10 disks, and the underlying storage operating system is responsible for allocating the blocks across the disks.
How BMS differs from other Cloud Environments
- Flexibility - Continue to run any Oracle version(s) you currently run on-premise. This enables you to re-create your environment (like-for-like) in the cloud. Since you own the environment, BMS helps you to avoid additional vendor lock-in associated with an Oracle Cloud migration
- Software License Savings - Mitigate additional licensing cost to migrate Oracle workloads to a virtualized cloud environment by up to 50%, or allow you to certify to own your ULA licenses in perpetuity.
- Unified Billing - Customers will receive one bill covering GCP, BMS, and Oracle licensing along with unified support from Google Cloud.
- High Bandwidth/ Low Latency Connectivity to Google - Google BMS Data centers are strategically placed next to existing GCP sites. Proximity to GCP data centers ensures low latency connection back to your Google project(s) along with other Google services.
How Can I Use Google Cloud BMS?
Lift and Shift
Replicate your exact on-prem environment in the cloud, “like-for-like”, providing the opportunity to easily “lift and shift” Oracle workloads and other legacy applications to the cloud.
Cost Savings
Avoid the cost of hiring specialized NetApp storage, networking, and server personnel by leveraging Google’s expertise. All facets of the BMS physical infrastructure are fully supported by Google.
High-Speed / Low Latency Peering with Google Cloud Platform
Since BMS is a Google service. These data centers are chosen for their proximity to existing Google data centers providing low-latency access to other Google services such as load balancing and other GCP services.
Geographical Control of Data
Although BMS is a cloud service, it is based in a physical data center within a region of your choice. This assists with regulatory and compliance requirements for frameworks such as GDPR and ITAR.
Disaster Recovery
Multiple BMS environments can be leveraged to create DR locations in separate regions for Geographical redundancy.
Will My Data be “Locked-In” to Google BMS
Google Cloud BMS is your personal colocation located in the Google Cloud. Since you are in control, backups and other data can be easily sent to other environments in a format of your choosing. Migrating to a new environment can be done just as easily as it would be in your on-prem data center.
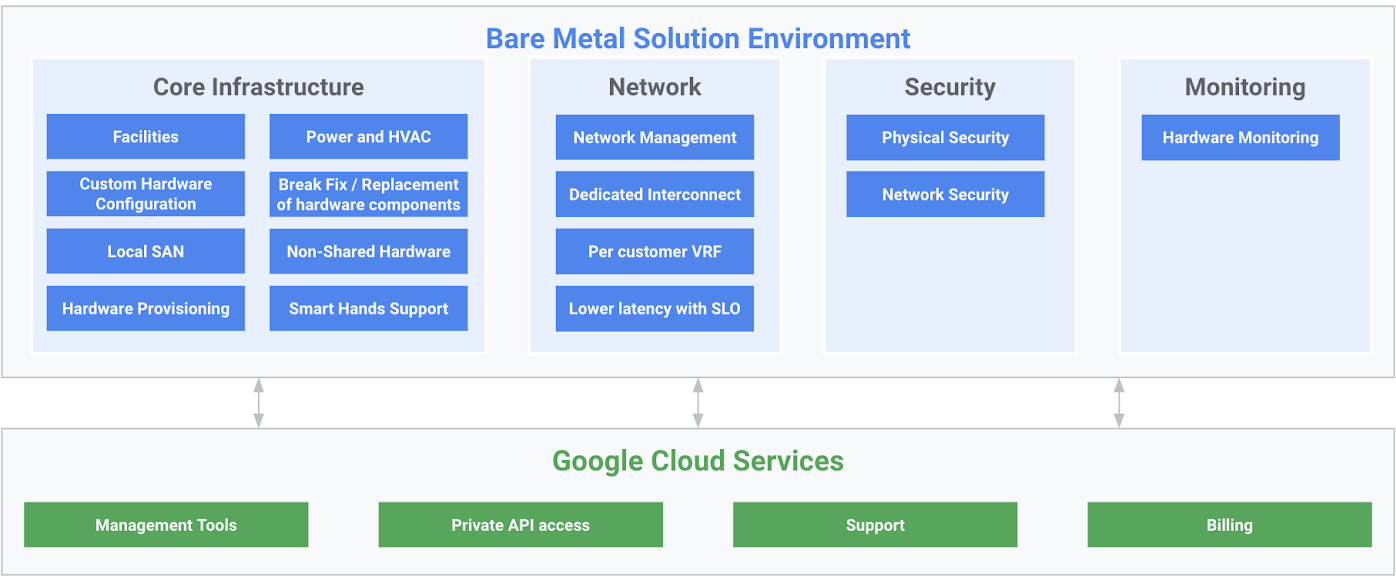
Responsibilities in Google BMS
Below is a quick summary of responsibilities in Google BMS:
| Google Responsibility | Customer Responsibility |
|---|---|
| Data Center space Power and cooling Break Fix / Replacement of hardware components Local SAN with IOPS SLO BIOS, controller, firmware patching Hardware provisioning Initial OS install Hard reboot/restart Network management Dedicated interconnect Low latency with SLO to Google Cloud (2 ms RT) Physical Security Network Security Hardware Monitoring Proactive maintenance (e.g. disk replacement) |
Licensing (bring your own license) BMS Core count for Database EE OS OS patching, Database patching, Application patching OS monitoring / Logging Oracle Database Administration and Monitoring Database installation Database Backup / Recovery / DR Application installation Google Cloud routes and firewall rules |
Copyright © Dito LLC, 2023